1. Fortune 500 Companies’ Kubernetes Secrets Unveiled in Public Repositories
Cybersecurity experts caution against the widespread exposure of Kubernetes configuration secrets in public repositories, posing a potential risk of supply chain attacks.
Aqua security researchers discovered encoded Kubernetes configuration secrets uploaded to public repositories, impacting top blockchain companies and various Fortune 500 firms.
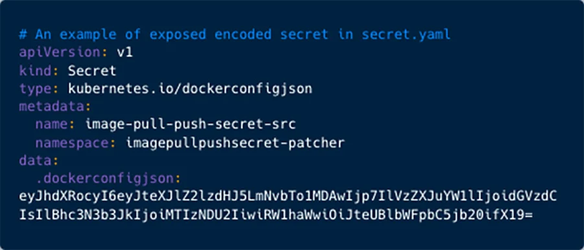
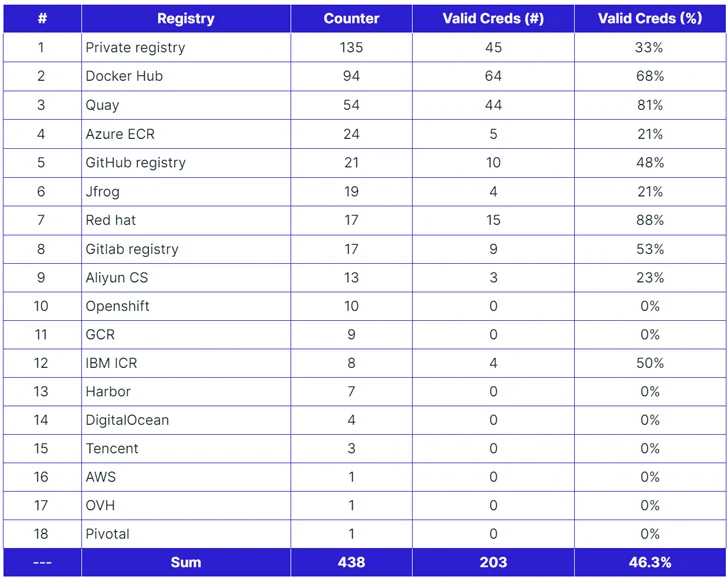
Out of 438 records, 46% contained valid credentials for container image registries, with 93 passwords manually set, often allowing both pulling and pushing privileges.
Nearly 50% of these passwords were identified as weak, emphasizing the urgent need for robust organizational password policies.
While some credentials were found to be temporary and expired,vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in container environments continue to be significant security concerns, as highlighted in Red Hat’s State of Kubernetes Security Report.
References
Kubernetes adoption, security, and market trends report 2023
Kubernetes Secrets of Fortune 500 Companies Exposed in Public Repositories
The Ticking Supply Chain Attack Bomb of Exposed Kubernetes Secrets
2. CVE-2023-46849, CVE-2023-46850: OpenVPN Access Server Vulnerabilities
OpenVPN Access Server, a widely-used VPN solution, has released an update (2.11.0 to 2.12.1) addressing two vulnerabilities (CVE-2023-46849 and CVE-2023-46850). These flaws in the OpenVPN 2.6 codebase may allow unauthorized access to sensitive data and potential Remote Code Execution.
While awaiting CVSS scores, users are advised to update their systems to mitigate security risks promptly.
CVE-2023-46849
CVE-2023-46849 is a “division by zero crash” flaw in the OpenVPN Access Server, occurring when the–fragment option is enabled in specific configurations of OpenVPN versions 2.6.0 to 2.6.6.
While this vulnerability could lead to a Denial-of-Service (DoS) and potential exposure of sensitive data, according to OpenVPN’s security advisory its exploitation on the Access Server is not straightforward due to the default configuration’s lack of the –fragment option.
Additionally, the control channel security adds an extra layer of complexity to potential exploitation.
CVE-2023-46850
CVE-2023-46850 involves a “Use After-Free Memory” security issue in the OpenVPN Access Server.This is a more serious vulnerability,as it has the potential to leak sensitive information from the server’s memory.
Attackers could exploit this issue to leak sensitive data through memory buffer leaks or execute Remote Code Execution (RCE) by sending network buffers to a remote peer. The severity of this vulnerability poses a considerable risk, offering attackers the opportunity to gain control over the affected server.
The security advisory on the OpenVPN community Wiki states,“OpenVPN 2.6 from v2.6.0 up to and including v.2.6.6 incorrectly use a send buffer after it has been free()d in some circumstances, causing some free()d memory to be sent to the peer. All configurations using TLS (e.g. not using–secret) are affected by this issue.”
Resolution
To safeguard your system, it is crucial to promptly update your OpenVPN Access Server to version 2.12.2 ora newer release, as these contain fixes for the identified vulnerabilities(CVE-2023-46849 and CVE-2023-46850).
Detailed instructions on how to perform the upgrade can be found in the provided resource: “Keeping OpenVPN Access Server Updated.” Taking this action will help mitigate the potential security risks associated with the vulnerabilities.
References
OpenVPN Security Advisory – Access Server Security Update (CVE-2023-46849, CVE-2023-46850)
SOCRadar – OpenVPN Access Server Vulnerabilities: Risk of Information Exposure, DoS, and RCE (CVE-2023-46849, CVE-2023-46850)
3. CVE-2023-46604: Apache ActiveMQ Flaw Being Exploited by Ransomware Group
Critical Alert: CVE-2023-46604, rated a perfect 10.0 on the CVSS scale, is an arbitrary code execution flaw tracked in Apache ActiveMQ. It could permit a threat actor to run arbitrary shell commands in memory.
Despite being patched in versions 5.15.16, 5.16.7, 5.17.6, and 5.18.3 last month, this flaw is actively exploited by ransomware groups deploying HelloKitty, and some strains similar to TellYouThePass, and the SparkRAT trojan.
VulnCheck reports attackers leveraging a publicly available POC, disclosed on Oct 25th, 2023, to exploit the vulnerability. The attacks utilize ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, a Spring framework class within ActiveMQ, to load a malicious XML bean configuration file over HTTP, achieving unauthenticated remote code execution.
“Now that we know attackers can execute stealthy attacks using CVE-2023-46604, it’s become even more important to patch your ActiveMQ servers and, ideally, remove them from the internet entirely,” said Jacob Baines, Chief Technology Officer at VulnCheck.
References
The Hacker News – New PoC Exploit for Apache ActiveMQ Flaw Could Let Attackers Fly Under the Radar
The Register – Critical Apache ActiveMQ flaw under attack by ‘clumsy’ ransomware crims
4. Sensitive Data at Risk: Critical Flaws in ownCloud File Sharing App
ownCloud, an open-source platform facilitating file sharing and synchronization in distributed enterprise settings, has recently disclosed three critical security vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities pose risks of unauthorized access, disclosure of sensitive information, and file modification.
The first vulnerability, identified as CVE-2023-49103 with a maximum CVSS v3 score of 10,was found in ownCloud/graphapi versions0.2.x before 0.2.1 and 0.3.x before 0.3.1.
It stems from a flaw in a third-party library (GetPhpInfo.php), revealing PHP environment configuration details upon access. In containerized deployments, this exposure may extend to critical data such as admin passwords, mail server credentials, and license keys.
The second issue, carrying a CVSS v3 score of 9.8, impacts ownCloud core library versions10.6.0 to 10.13.0. This flaw permits unauthorized access, modification, or deletion of any file without authentication, provided the user’s username is known, and no signing key has been configured.
The third, less severe vulnerability (CVSS v3 score: 9) involves a subdomain validation bypass affecting all versions of the oauth2 library below 0.6.1. In theoauth2 app, attackers can exploit this flaw by inputting a specially crafted redirect URL, thereby bypassing validation and redirecting callbacks to a domain controlled by the attacker.
Resolution
- As recommended by ownCloud, delete the”owncloud/apps/graphapi/vendor/microsoft/microsoft-graph/tests/GetPhpInfo.php” file and disable the “phpinfo” function.
- Change secrets like the ownCloud admin password, mail server and database credentials, and Object-Store/S3 access keys.
- Deny the use of pre-signed URLs if no signing key is configured for the owner of the files.
- Harden the validation code in theOauth2 app.
- Temporary solution: disable the “Allow Subdomains” option.




